Delving into the fascinating world of plant reproduction, the gizmo flower pollination answer key unveils the intricate mechanisms behind the pollination process. This comprehensive resource provides a profound understanding of the methods, factors, and strategies involved in ensuring successful pollination.
By exploring the key concepts and variables within the Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation, this guide empowers individuals to analyze data, identify patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions about pollination ecology.
Gizmo Flower Pollination Overview
The Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation is a virtual environment that allows students to explore the process of flower pollination. The simulation includes a variety of different flower species, each with its own unique characteristics. Students can use the simulation to investigate how different factors, such as the presence of pollinators, the distance between flowers, and the weather, affect the rate of pollination.
The objectives of the Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation are to:
- Learn about the process of flower pollination.
- Investigate how different factors affect the rate of pollination.
li>Develop an understanding of the importance of pollination for plant reproduction.
Key Concepts
The Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation explores a number of key concepts, including:
- The structure and function of flowers.
- The role of pollinators in the pollination process.
- The factors that affect the rate of pollination.
- The importance of pollination for plant reproduction.
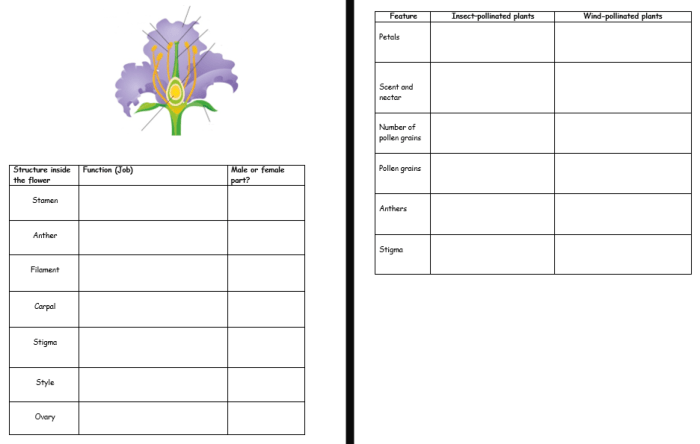
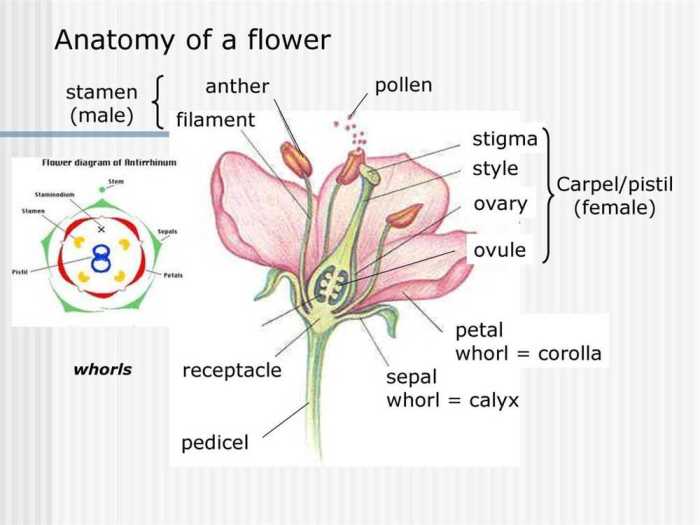
Pollination Process
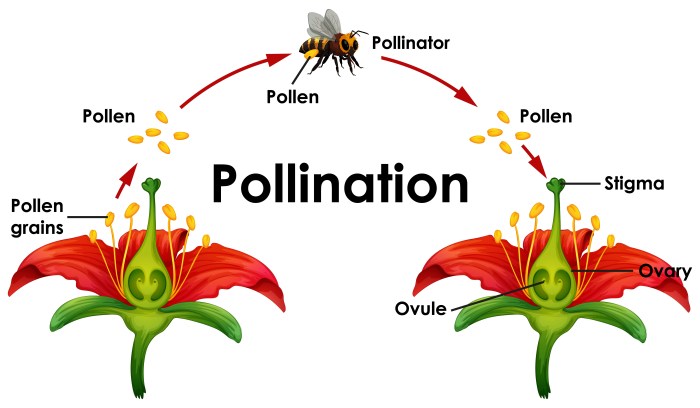
Pollination is the process of transferring pollen from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of the same or another flower. This process is essential for the reproduction of flowering plants, as it allows the pollen to reach the female reproductive organs and fertilize the ovules.
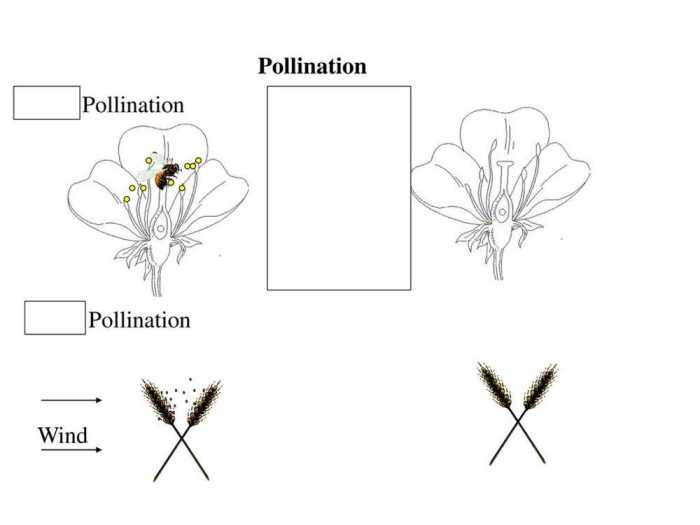
There are three main methods of pollination illustrated in the simulation:
- Wind pollinationoccurs when pollen is carried by the wind from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. This method of pollination is most common in plants that have small, lightweight pollen grains, such as grasses and trees.
- Insect pollinationoccurs when pollen is carried by insects from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. This method of pollination is most common in plants that have large, sticky pollen grains, such as roses and sunflowers.
- Water pollinationoccurs when pollen is carried by water from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. This method of pollination is most common in plants that live in aquatic environments, such as water lilies and pondweeds.
Pollinators play a vital role in the pollination process. They are responsible for transferring pollen from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. Pollinators include insects, such as bees, butterflies, and moths, as well as birds, bats, and even the wind.
There are a number of factors that can affect pollination success. These factors include:
- The availability of pollinators
- The weather conditions
- The health of the flowers
- The distance between flowers
Pollination is a vital process for the reproduction of flowering plants. It is essential for the production of seeds, which are necessary for the germination of new plants. Pollination also helps to maintain genetic diversity within plant populations.
Simulation Variables
The Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation allows users to investigate the factors that affect pollination. The simulation includes several variables that can be manipulated to observe their effects on the pollination process.
The independent variables in the simulation are those that can be controlled by the user. These variables include:
- Number of flowers
- Number of bees
- Pollen production
- Nectar production
- Wind speed
The dependent variables in the simulation are those that are affected by the independent variables. These variables include:
- Pollination rate
- Seed production
- Flower color
Changing the independent variables can have a significant impact on the dependent variables. For example, increasing the number of flowers can increase the pollination rate and seed production. Increasing the number of bees can also increase the pollination rate, but it can also decrease the amount of nectar available for each bee.
Changing the pollen production or nectar production can affect the attractiveness of the flowers to bees, which can in turn affect the pollination rate.
Limitations of the Simulation, Gizmo flower pollination answer key
The Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation is a valuable tool for investigating the factors that affect pollination. However, it is important to note that the simulation has some limitations. These limitations include:
- The simulation does not take into account the effects of other pollinators, such as birds, bats, and insects.
- The simulation does not take into account the effects of weather conditions, such as rain and wind.
- The simulation does not take into account the effects of plant diseases and pests.
Despite these limitations, the Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation can be a useful tool for understanding the basic principles of pollination.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Analyzing data from the Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation helps identify patterns and trends in pollination ecology. To organize the collected data, create an HTML table with columns for variables such as flower type, pollinator type, number of visits, and number of successful pollinations.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Examine the data to identify patterns and trends. For example, compare the number of visits and successful pollinations for different flower types. Are certain flower types more attractive to pollinators? Do specific pollinator types have higher success rates in pollinating certain flowers? Additionally, consider the effect of environmental factors on pollination success.
Implications for Pollination Ecology
The data analysis provides insights into pollination ecology. It helps determine which flower and pollinator combinations are most effective in pollination. This information is crucial for understanding plant-pollinator interactions, assessing the impact of environmental changes on pollination, and developing conservation strategies to protect pollinators and ensure successful plant reproduction.
Pollination Strategies
Plants employ diverse pollination strategies to ensure successful reproduction. These strategies enhance the chances of pollen transfer from the anthers to the stigmas, maximizing the likelihood of fertilization and seed production.
Pollination strategies can be broadly classified into two main categories: biotic and abiotic pollination.
Biotic Pollination
Biotic pollination involves the transfer of pollen by living organisms, primarily insects, birds, bats, and other animals. This type of pollination is highly specific, with plants evolving adaptations to attract and reward specific pollinators.
- Entomophily: Pollination by insects, such as bees, butterflies, and moths. Plants attract insects through colorful petals, nectar production, and specific scents.
- Ornithophily: Pollination by birds, such as hummingbirds and sunbirds. Plants offer nectar-rich flowers with bright colors and long, tubular shapes.
- Chiropterophily: Pollination by bats. Flowers pollinated by bats are typically white or pale-colored, with a strong, musky scent.
Abiotic Pollination
Abiotic pollination occurs without the involvement of living organisms. The two main forms of abiotic pollination are:
- Anemophily: Pollination by wind. Plants pollinated by wind produce large amounts of lightweight pollen that can be easily carried by air currents.
- Hydrophily: Pollination by water. This is a rare form of pollination found in aquatic plants. Pollen is released into the water and carried to the stigmas of submerged flowers.
The choice of pollination strategy by a plant depends on various factors, including the availability of pollinators, the size and shape of the flowers, and the environmental conditions.
Importance of Pollination: Gizmo Flower Pollination Answer Key
Pollination is a vital ecological and economic process that plays a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and sustaining food production worldwide.
Ecological Importance
- Plant reproduction:Pollination facilitates the transfer of pollen from the male anthers to the female stigmas of flowers, enabling fertilization and seed production.
- Biodiversity:Pollination supports the survival and reproduction of diverse plant species, ensuring genetic diversity and ecological stability.
- Food chain:Plants pollinated by insects, birds, and mammals provide food and shelter for a wide range of animals, including many threatened species.
Economic Importance
- Food security:Approximately 75% of the world’s food crops depend on pollination by insects, birds, and other animals.
- Agriculture:Pollinators enhance crop yields and quality, reducing the need for expensive artificial pollination methods.
- Medicines:Many plants used in traditional and modern medicine rely on pollination for their production.
Threats to Pollinators and their Impact on Pollination
Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, face numerous threats, including:
- Habitat loss:Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion destroy or fragment pollinator habitats.
- Pesticides and herbicides:Chemicals used in agriculture can kill or harm pollinators, disrupting their populations.
- Climate change:Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can affect pollinator behavior and availability.
These threats can lead to:
- Reduced pollination efficiency:Fewer pollinators result in lower pollination rates and reduced crop yields.
- Loss of plant diversity:Without pollinators, some plant species may decline or even become extinct.
- Economic losses:Reduced pollination can lead to significant economic losses in agriculture and other industries.
Conservation Measures to Protect Pollinators and Ensure Successful Pollination
Protecting pollinators is essential for maintaining pollination services and ensuring the health of ecosystems and food production.
- Habitat protection:Preserving and restoring pollinator habitats, such as meadows, forests, and wetlands.
- Sustainable agriculture:Using integrated pest management practices that minimize the use of harmful chemicals.
- Public awareness:Educating the public about the importance of pollinators and encouraging pollinator-friendly practices.
- Research and monitoring:Conducting research to understand pollinator biology and threats, and monitoring pollinator populations to track trends.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of the Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation?
The Gizmo Flower Pollination simulation aims to illustrate the various methods of pollination and the factors that influence its success, providing insights into the ecological interactions between plants and pollinators.
How can I use the gizmo flower pollination answer key?
The gizmo flower pollination answer key provides detailed explanations and guidance for each aspect of the simulation, assisting users in understanding the concepts and analyzing the data generated.
What are the key concepts explored in the simulation?
The simulation explores concepts such as the different methods of pollination, the role of pollinators, the factors affecting pollination success, and the adaptations plants have evolved to attract specific pollinators.