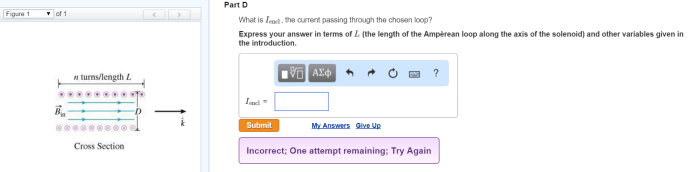
What is iencl the current passing through the chosen loop – IENCL, an acronym for “Induced Electromotive Force in a Closed Loop,” represents the current passing through a chosen loop in an electrical circuit. Understanding IENCL is crucial for circuit analysis, design, and optimization.
This comprehensive guide explores the concept of IENCL, its measurement, and its applications in electrical engineering.
Definition of IENCL
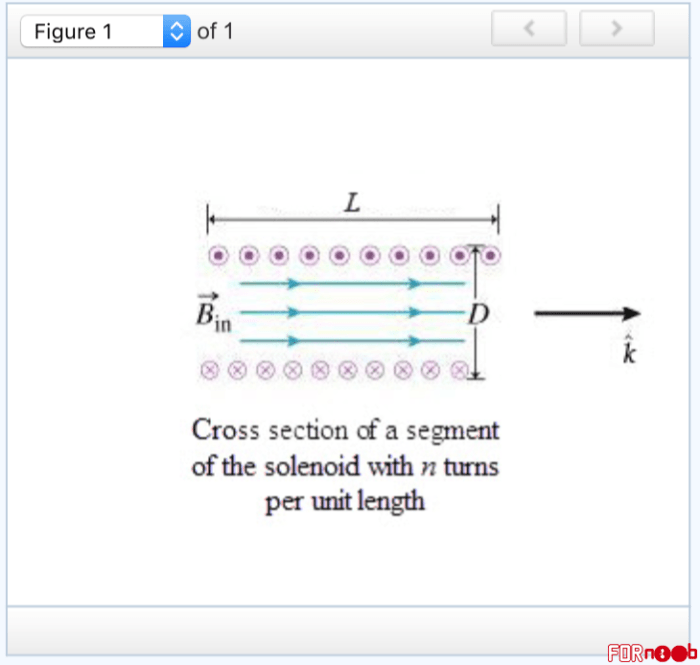
IENCL stands for Induced Electromotive Force Current Loop. It refers to the current induced in a loop of wire when it is placed in a changing magnetic field. The current flow is caused by the electromotive force (EMF) generated within the loop due to electromagnetic induction.
Types of Loops
In electrical circuits, various types of loops are used, each with specific characteristics and applications:
-
-*Closed Loops
These loops form a complete path for current flow, with no open ends. They are commonly used in power distribution systems and electronic circuits.
-*Open Loops
Open loops have one or more breaks in the current path, preventing continuous current flow. They are often used in control systems and signal processing applications.
-*Ground Loops
Ground loops are unintentional loops formed by the connection of multiple electrical devices to a common ground reference. They can cause noise and interference in electronic systems.
-*Resonant Loops
Resonant loops are tuned circuits that exhibit resonance at specific frequencies. They are used in radio frequency (RF) circuits, filters, and oscillators.
Factors Affecting IENCL
The current passing through a loop is influenced by several factors:
-
-*Magnetic Field Strength
The strength of the magnetic field surrounding the loop directly affects the induced EMF and, consequently, the current flow.
-*Loop Area
The larger the area enclosed by the loop, the greater the amount of magnetic flux passing through it, leading to higher induced EMF and current.
-*Rate of Magnetic Field Change
The rate at which the magnetic field changes over time determines the magnitude of the induced EMF and current. Rapid changes result in higher EMF and current.
-*Loop Resistance
The resistance of the loop itself affects the current flow. Higher resistance impedes current flow, while lower resistance allows for higher current.
Measurement and Analysis of IENCL, What is iencl the current passing through the chosen loop
IENCL can be measured using various techniques, including:
-
-*Voltmeters
Voltmeters measure the EMF induced in the loop, which is directly proportional to the current flow.
-*Ammeters
Ammeters measure the current passing through the loop directly.
-*Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes can display the waveform of the induced EMF or current, providing insights into their temporal characteristics.
Applications of IENCL
IENCL has numerous practical applications in electrical engineering:
-
-*Electric Motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy by utilizing the principle of IENCL. The current passing through the motor’s windings creates a magnetic field that interacts with the motor’s permanent magnets, resulting in rotation.
-*Generators
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by exploiting IENCL. The rotation of the generator’s armature within a magnetic field induces an EMF and current in the windings.
-*Transformers
Transformers use IENCL to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through magnetic coupling. The primary winding induces an EMF in the secondary winding, which results in current flow in the secondary circuit.
Helpful Answers: What Is Iencl The Current Passing Through The Chosen Loop
What factors influence IENCL?
Factors affecting IENCL include loop resistance, magnetic field strength, and loop area.
How is IENCL measured?
IENCL can be measured using a fluxmeter or by calculating the change in magnetic flux linked with the loop.