Automatic expansion valves are good at maintaining a constant – Automatic expansion valves play a crucial role in maintaining a constant refrigerant flow rate, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in various industrial and commercial refrigeration systems. Their ability to regulate refrigerant flow precisely contributes to enhanced system reliability, reduced energy consumption, and improved overall system performance.
This article delves into the design, operation, and advantages of automatic expansion valves, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance in modern refrigeration systems.
Applications and Advantages
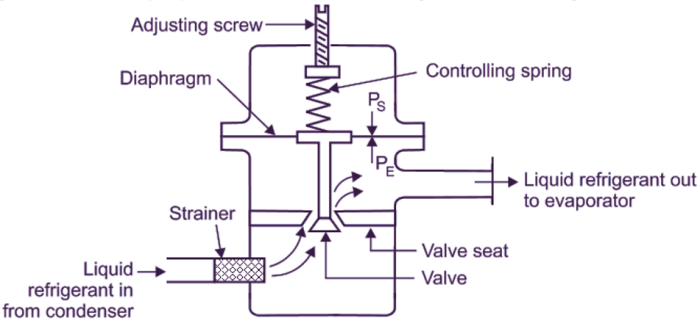
Automatic expansion valves (AXVs) play a crucial role in refrigeration and air conditioning systems by maintaining a constant refrigerant flow rate, ensuring optimal system performance. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to adjust the flow of refrigerant based on changing system conditions, leading to several benefits:
- Precise Control:AXVs precisely regulate refrigerant flow, ensuring that the evaporator is always supplied with the optimal amount of refrigerant, resulting in improved system efficiency and cooling capacity.
- Energy Efficiency:By maintaining a constant superheat or pressure at the evaporator outlet, AXVs minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs.
- Extended System Life:Proper refrigerant flow prevents the evaporator from freezing or overheating, extending the lifespan of the system components.
AXVs are widely used in various industries and systems, including:
- Refrigeration systems (e.g., cold storage, food processing)
- Air conditioning systems (e.g., residential, commercial, industrial)
- Heat pumps
Compared to other types of expansion valves, AXVs offer several advantages:
- Automated Control:AXVs automatically adjust refrigerant flow based on system conditions, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- Improved Accuracy:Electronic or mechanical sensing elements provide precise control, resulting in better system performance.
- Flexibility:AXVs can be adapted to various system configurations and refrigerants, offering greater versatility.
Design and Components: Automatic Expansion Valves Are Good At Maintaining A Constant

An AXV consists of several key components that work together to regulate refrigerant flow:
- Sensing Element:The sensing element measures the superheat or pressure at the evaporator outlet and sends a signal to the power element.
- Diaphragm:The diaphragm separates the sensing element from the power element and controls the flow of refrigerant through the valve.
- Power Element:The power element receives the signal from the sensing element and adjusts the position of the diaphragm to regulate refrigerant flow.
Different types of sensing elements are used in AXVs, each with its own characteristics:
- Thermal Expansion Bulb:A bulb filled with refrigerant vapor that expands or contracts with temperature changes, altering the pressure on the diaphragm.
- Electronic Temperature Sensor:Measures temperature directly and sends an electrical signal to the power element.
- Pressure Transducer:Measures pressure at the evaporator outlet and sends a signal to the power element.
Operation and Control

AXVs maintain a constant superheat or pressure at the evaporator outlet by adjusting refrigerant flow. Superheat refers to the temperature difference between the refrigerant vapor and the saturated vapor temperature at the evaporator outlet.
AXVs use different control strategies to maintain the desired superheat or pressure:
- Proportional-Integral (PI):Adjusts the valve position based on the error between the measured and desired superheat or pressure.
- Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID):Similar to PI, but also includes a derivative term to improve response time.
- Fuzzy Logic:Uses a set of rules to determine the valve position based on multiple inputs, such as superheat, pressure, and system load.
| Control Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| PI | Simple to implement, stable operation | Slow response to changes, steady-state error |
| PID | Faster response, reduced steady-state error | More complex to tune, potential for instability |
| Fuzzy Logic | Adaptive to changing conditions, robust performance | Requires expert knowledge to design and implement |
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
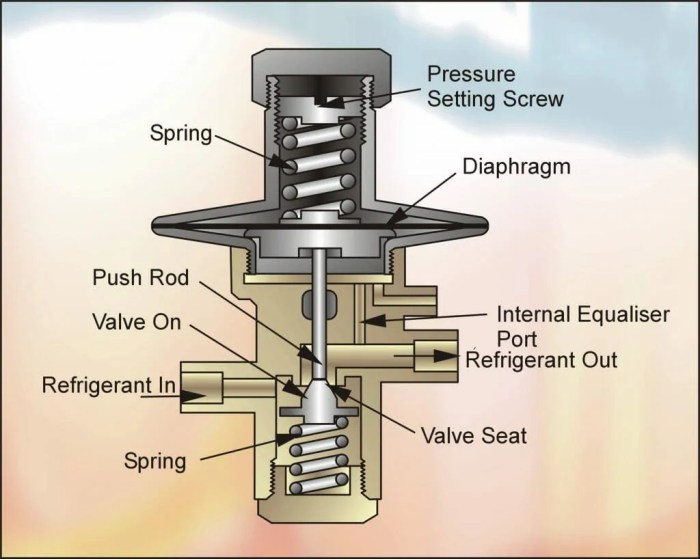
Common problems that can occur with AXVs include:
- Clogged Valve:Debris or dirt can accumulate in the valve, restricting refrigerant flow.
- Damaged Diaphragm:A torn or damaged diaphragm can lead to refrigerant leaks.
- Faulty Sensing Element:Incorrect readings from the sensing element can result in improper refrigerant flow.
Troubleshooting tips for AXVs:
- Check for Clogs:Inspect the valve and inlet/outlet lines for any blockages.
- Examine the Diaphragm:Look for any tears or damage to the diaphragm.
- Test the Sensing Element:Use a multimeter or temperature probe to verify the accuracy of the sensing element.
Regular maintenance and calibration are essential for optimal AXV performance:
- Inspect and Clean:Regularly inspect the valve and clean any dirt or debris.
- Calibrate:Calibrate the sensing element and power element periodically to ensure accurate refrigerant flow control.
- Replace Components:Replace worn or damaged components as necessary.
FAQ Compilation
What are the key advantages of using automatic expansion valves?
Automatic expansion valves offer several advantages, including precise flow control, reduced energy consumption, improved system reliability, and enhanced overall system performance.
How do automatic expansion valves maintain a constant refrigerant flow rate?
Automatic expansion valves utilize a sensing element to monitor the superheat or pressure at the evaporator outlet. The sensing element sends a signal to the power element, which adjusts the valve opening to maintain the desired flow rate.
What are the different types of sensing elements used in automatic expansion valves?
Common sensing elements used in automatic expansion valves include thermostatic elements, electronic sensors, and mechanical diaphragms. Each type has its own characteristics and applications.