Ap bio diffusion and osmosis lab answers – AP Biology Diffusion and Osmosis Lab Answers embarks on an enlightening journey, providing a thorough understanding of these fundamental biological processes. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of diffusion and osmosis, empowering students with a deep appreciation for their significance in living organisms.
Through a meticulously crafted exploration, this resource delves into the mechanisms, applications, and experimental techniques surrounding diffusion and osmosis. Its authoritative tone and engaging narrative captivate readers, fostering a profound understanding of these essential concepts.
Diffusion and Osmosis Basics: Ap Bio Diffusion And Osmosis Lab Answers
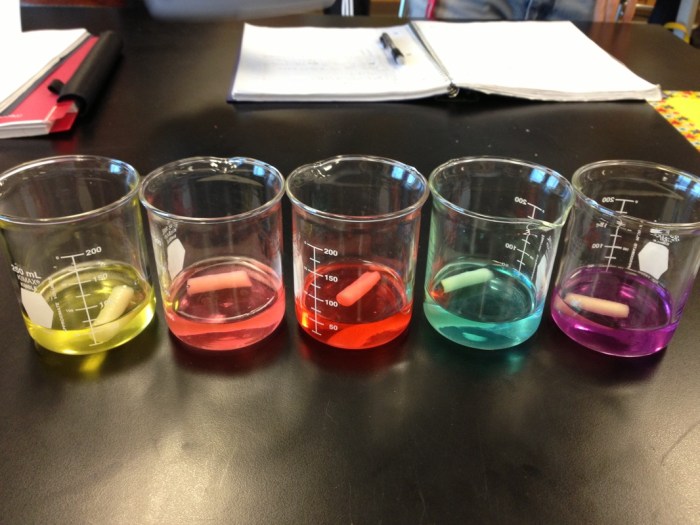

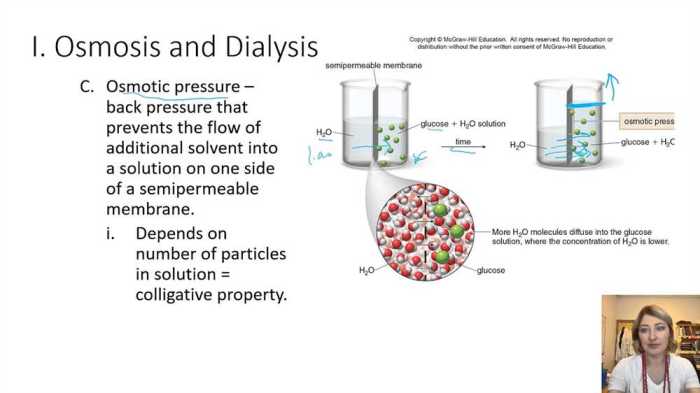
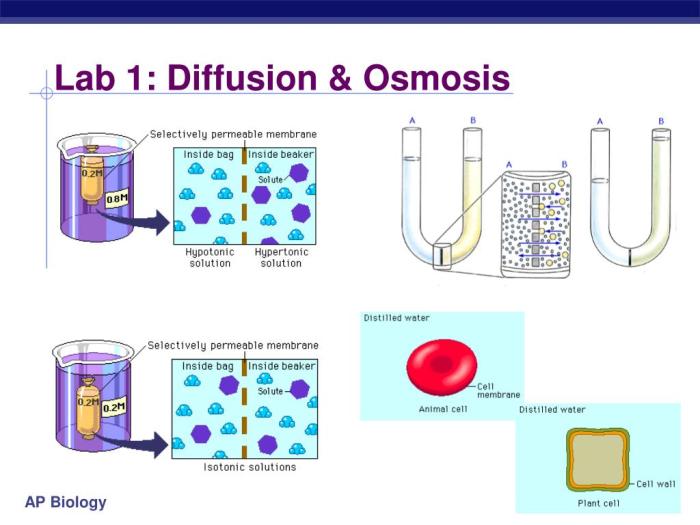
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs naturally and is essential for the survival of cells and organisms. Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
Understanding the principles of diffusion and osmosis is crucial for comprehending various biological processes.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Diffusion and Osmosis, Ap bio diffusion and osmosis lab answers
- Concentration gradient: The greater the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of diffusion or osmosis.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to a faster rate of diffusion and osmosis.
- Surface area: A larger surface area increases the number of molecules that can diffuse or osmose, resulting in a faster rate.
- Distance: The shorter the distance between the areas of different concentrations, the faster the rate of diffusion or osmosis.
Experimental Design
Designing an experiment to investigate diffusion and osmosis involves carefully controlling variables to observe their effects on the rate of these processes.
Independent and Dependent Variables
The independent variable is the factor being manipulated in the experiment, while the dependent variable is the factor being measured.
In a diffusion experiment, the independent variable could be the concentration gradient, temperature, or surface area. The dependent variable would be the rate of diffusion.
In an osmosis experiment, the independent variable could be the concentration of the solute, the temperature, or the type of membrane. The dependent variable would be the rate of osmosis.
Controls
Controls are essential in any experiment to ensure that the results are valid. In a diffusion or osmosis experiment, a control group is used to compare the results of the experimental group.
The control group should be identical to the experimental group in all respects except for the independent variable. This allows the researcher to isolate the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis are crucial steps in any experiment. In a diffusion or osmosis experiment, data can be collected using various methods, such as:
- Measuring the change in concentration over time
- Measuring the change in volume over time
- Using a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of a solution
Once the data is collected, it can be analyzed to determine the rate of diffusion or osmosis. This can be done using a variety of statistical methods, such as:
- Linear regression
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Chi-square test
The results of the statistical analysis can be used to draw conclusions about the effects of the independent variable on the rate of diffusion or osmosis.
| Independent Variable | Dependent Variable | Control Group | Experimental Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration gradient | Rate of diffusion | No concentration gradient | Concentration gradient present |
| Temperature | Rate of osmosis | Constant temperature | Variable temperature |
| Type of membrane | Rate of osmosis | Semipermeable membrane | Non-permeable membrane |
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are essential processes in many biological systems. They play a role in:
- The exchange of nutrients and waste products between cells
- The regulation of water balance in plants and animals
- The transport of molecules across cell membranes
Diffusion and osmosis are also used in a variety of medical applications, such as:
- The delivery of drugs to specific parts of the body
- The removal of toxins from the body
- The diagnosis of diseases
Extensions
There are many ways to extend the investigation of diffusion and osmosis. Some potential research questions include:
- How does the rate of diffusion or osmosis change in different environments?
- What are the effects of different types of molecules on the rate of diffusion or osmosis?
- How can diffusion and osmosis be used to improve medical treatments?
One possible follow-up experiment could investigate the effects of different types of membranes on the rate of osmosis. This experiment could be designed to test the hypothesis that the rate of osmosis is faster across a semipermeable membrane than across a non-permeable membrane.
Top FAQs
What are the key differences between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
How do factors like temperature and concentration affect the rate of diffusion?
Higher temperatures and greater concentration gradients accelerate the rate of diffusion, as they increase the kinetic energy and number of molecules available for movement.
What are some real-world applications of diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion plays a crucial role in gas exchange in the lungs, nutrient absorption in the digestive system, and waste removal in the kidneys. Osmosis is essential for maintaining water balance in cells and tissues, as well as for the uptake of water by plants.